Description
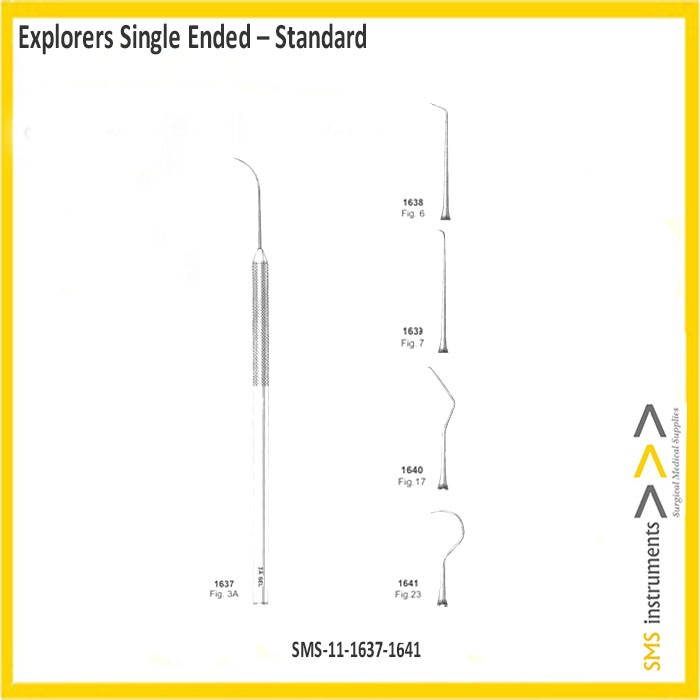
Explorers Single Ended Standard
Size:
1637 – Fig 3A
1638 – Fig 6
1639 – Fig 7
1640 – Fig 17
1641 – Fig 23
Dental Instruments
Explorer # 3A
SMS Explorer #3A Single ended provides the tactile information to the clinician’s fingers and is used to locate calculus deposits, tooth surface irregularities, defective margins on restorations, decalcified areas and carious lesions. This product features an Textured handle.
Explorer # 6, 17, 23
SMS Single ended explorer used in the detection of decay and calculus, exploration of pocket characteristics, furcations and restorations. This product features an Textured handle.
| Surname | Explorer |
| Tip Configuration | Pointed |
| Size / Model / Figure | No. 3A, 6, 7, 17, 23 |
| curvature | Angled & Curved |
| Handle | Textured |
| Finishing | Mirror Polish Finishing |
| Instrument Type | Dental Explorer |
| Material | Stainless Steel |
| Disposable or Reusable | Reusable |
| Rusting Prevention | Passivation Processed |
| Cleaning | Ultrasonic Cleaned |
| Sterile or Non-Sterile | Non-Sterile |
| Latex or Latex-Free | Latex-Free |
| Test Performed | Boil, Shape & Performance Test |
| Grade | Premium OR-Grade |
| Packing | Individually Packed in SMS Brand printed Poly-sleeve |
A Dental Explorer is an instrument in dentistry commonly used in the dental armamentarium. A sharp point at the end of the explorer is used to enhance tactile sensation. The dental explorer or probe, is a sharp-ended instrument.
It is used to check for hard tissue defects, for example:
- To determine the presence ofcaries
- To explore otherenamel and dentin defects, such as fractured teeth and odontoclastic resorptive lesions
The explorer is also useful for tactile examination of the subgingival tooth surfaces. Subgingival calculus and odontoclastic resorptive lesions may be identified in this way. Dental explorers are available in various shapes, usually straight or curved.
Types
These are delicate, pointed instruments used for tactile examination of tooth surfaces and restorations to identify any irregularities. They are of 3 types
- Straight Explorer (Left) & Curved Explorer (Right)
- Straight explorer is bent at 90 degrees. It is used to examine the occusal / top surface of teeth for tooth decay.
- Curved explorer is curved like a half-moon and the exploring tip is at right angles to the handle. It is also called the “Shepherd’s crook” explorer. It is also used to examine the occusal / top surface of teeth for tooth decay.
This explorer has 2 or more angles in the shank and exploring tip is pointed towards the handle. It is useful in examining the proximal/ side surfaces of the teeth for detecting caries.
Design of Explorer
- Explorer are made of flexible metal that conducts vibrations from the working end to the clinician fingers on instrument shank and handle.
- Circular in cross- section
- Working end is 1-2mm length and is referred to as the explorer tip
- The actual point of the explorer is not used to detect the calculus, rather the side of the explorer tip is applied to the tooth surface.
Function of Explorers
- Explorer are used to detect, by tactile means, the texture and character of tooth surfaces, before, during and after periodontal debridement to assess the progress and completeness of instrumentation.
- Explorer are used to examine tooth surface for calculus, decalcified and carious lesions, dental anomalies and anatomic features such as grooves, curvatures, or root furcations.